Sympathetic Preganglionic Fibers Release Which Neurotransmitter
Which neurotransmitter is released from postganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nervous system. Emotional state of the individual.
Function of the postsynaptic receptor to which it targets B.

. The nicotinic receptor is a ligand-gated cation channel that results in depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane. The preganglionic nerves synapse in the sympathetic chain and long postganglionic nerves innervate the final target. So this means there is preganglionic and postganglionic release of neurotransmitterSympathetic.
However in the sympathetic system postganglionic are not all the same. The neurotransmitter released by the postganglionic fibers of the sympathetic division is. Neurotransmitters These are the chemicals released by the axons at the nerve terminals.
These neurons of the sympathetic nervous system are adrenergic using noradrenaline as the neurotransmitter while the preganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic nervous system are cholinergic using acetylcholine as the neurotransmitter. These include all preganglionic fibers of the ANS. Terminal This problem has been solved.
Sympathetic fight or flight - stressful 2. Both sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic neurons are cholinergic meaning they release acetylcholine Ach at the synapse in the ganglion. As stated earlier the sympathetic system has thoracolumbar outflow with short pre-ganglionic fibers.
These neurotransmitters are released at a location known as the synapse which is a junction point between the axon of one nerve cell and the dendrite of another. Therefore these neurons use acetylcholine as the neurotransmitterAt the synapses that are present within the ganglia preganglionic nerve fibers release acetylcholine that involves the activation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors present in the postganglionic neurons. In response to stress the sympathetic efferent nerves send brain signals to preganglionic nerve fibers to activate the adrenal gland to release catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline.
The will be a preganglionic fiber and a post ganglionic fiber. Both preganglionic and postganglionic neurons are multipolar. At the synapses within the ganglia the preganglionic neurons release acetylcholine a neurotransmitter that activates nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on postganglionic neurons.
The first set called preganglionic neurons originates in the brainstem or the spinal cord and the second set called ganglion cells or postganglionic neurons lies outside the central nervous system in collections of nerve cells called autonomic ganglia. Ganglion containing the preganglionic fiber E. The autonomic system is divided into two systems.
Norepinephrine Which neurotransmitter is released from preganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nervous system. See the answer Show transcribed image text. Other articles where preganglionic neuron is discussed.
Note that the term postganglionic neuron may be used to describe the projection from a ganglion to the target. Autonomic Nervous System ANS Neurotransmitters December 6 2015 medusmle ANS controls involuntary activity. Parasympathetic system postganglionic axons release ACh.
The sympathetic preganglionic neurons SPNs lie within the spinal cord and their axons traverse the ventral horn to exit in ventral roots where they form synapses onto postganglionic neurons. Preganglionic components Lateral horn of. Both sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic neurons are cholinergic meaning they release acetylcholine Ach at the synapse in the ganglion.
The axons leave the ganglia and project onto visceral effectors where they release the neurotransmitter norepinephrine. Norepinephrine Which half of the autonomic nervous. In the autonomic nervous system all preganglionic fibers release the neurotransmitter.
Sympathetic preganglionic fibers tend to be shorter than parasympathetic preganglionic fibers because sympathetic ganglia are often closer to the spinal cord than are. Thus these neurons are the last point at which the central nervous system can exert an effect to enable changes in sympathetic outflow. Norepinephrine in the autonimic nervous system most sympathetic postganglionic fibers release the neurotransmitter.
Parasympathetic rest and digest - peaceful In both of these systems we will see a two neuron system. One major function of catecholamines is to increase blood pressure and divert blood flow from the GI tract to the muscle and brain which serves to promote an immediate fight or flight. Related Question Answers.
All preganglionic fibers both sympathetic and parasympathetic release ACh. All preganglionic fibers whether they are in the sympathetic division or in the parasympathetic division are cholinergic that is these fibers use acetylcholine as their neurotransmitter and they are myelinated. All preganglionic fibers release Acetylcholine ACh that has Nicotinic receptors in both the parasympathetic and sympathetic ganglia.
Acetylcholine is the preganglionic nerve neurotransmitter and norepinephrine is the postganglionic neurotransmitter except for the sweat glands which have a sympathetic cholinergic innervation. The autonomic nervous system. Parasympathetic is CranioSacral has long preganglionic and short postgnglionic fibers.
All ganglionic neuronsthe targets of these preganglionic fibershave nicotinic receptors in their cell membranes. Ganglion where the postganglionic fiber originates D. Preganglionic fibers release ACh postganglionic fibers release norepinephrine or ACh at effectors effect is either stimulatory or inhibitory depending on type of receptors.
These fibers are unmyelinated. What neurotransmitter is released by preganglionic and postganglionic parasympathetic neurons. In the parasympathetic system postganglionic neurons are also cholinergic.
The excitatory or inhibitory effect of a postganglionic sympathetic fiber is determined by which of the following features or structures. So the ganglia of the sympathetic system are also present along the thoracic and lumbar segments of the spinal cord. A acetylcholine B norepinephrine C serotonin D dopamine E GABA 65.
- sympathetic postganglionic axons release. Specific organ innervated C. In the autonomic nervous system most sympathetic postganglionic fibers release the neurotransmitter.
Compared with the preganglionic fibers postganglionic sympathetic fibers are long because of the relatively greater distance from the ganglion to the target effector. All autonomic preganglionic fibers release Acetylcholine. In the parasympathetic system postganglionic neurons are also cholinergic.

Solved What Neurotransmitter Is Released From The Chegg Com

Autonomic Nervous System Physiology An Illustrated Review

Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic And Parasympathetic Response Function And Definition Ezmed

Cv Pharmacology Autonomic Ganglia
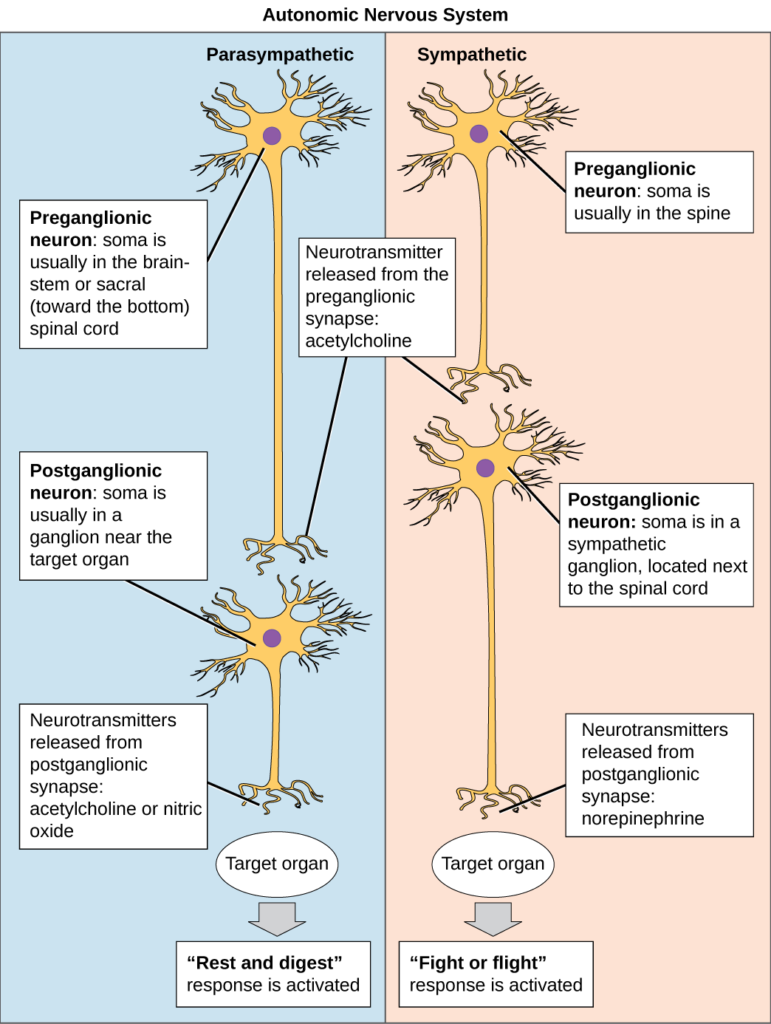
Autonomic Nervous System Biology For Majors Ii

Cv Pharmacology Autonomic Ganglia

Structure Of The Autonomic Nervous System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology

Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Flashcards Quizlet

Structure Of The Autonomic Nervous System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology

Anatomy 1 Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Flashcards Quizlet

Autonomic Nervous System Ppt Download

Pharmacology Of Ans Ii Sympathetics Flashcards Quizlet
5 Autonomic Nervous System Functions Of Cells And Human Body

Synaptic Physiology Of The Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous System The Nervous System Medical Physiology 3rd Edition

Autonomic Nervous System Basicmedical Key

Acetylcholine Definition Function Facts Britannica

Neurotransmitter Effects All Neurons Release Which Has An In The Ans Preganglionic Fibers Postganglionic Ppt Download
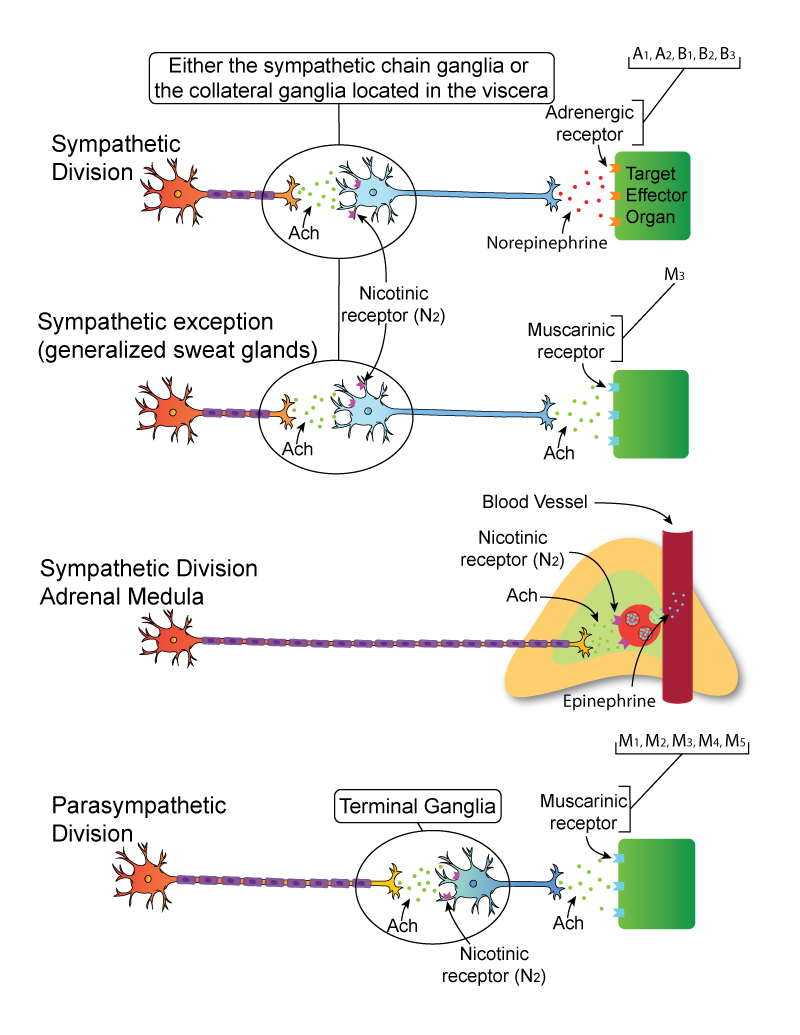
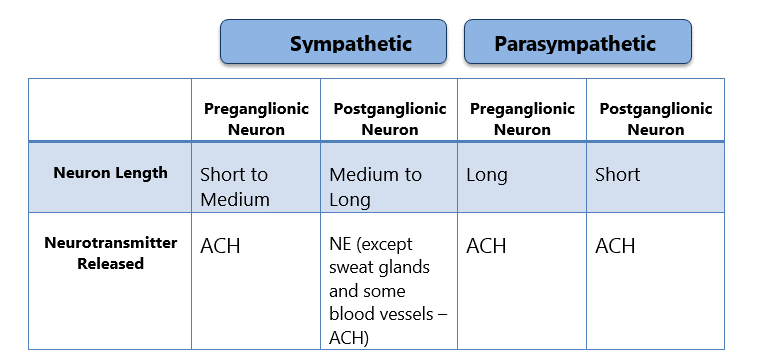

Comments
Post a Comment