Which of the Following Are Indicators of Renal Function
Used to monitor the progression of renal disease or to screen for occult renal insufficiency. Chronic kidney disease refers to the gradual loss of kidney function in the early stages its common for very few signs or symptoms to appear.

Diabetic Kidney Disease American Society Of Nephrology
Urea clearance is a poor indicator of glomerular filtration rate as its overproduction rate depends on several non.

. Blood andor protein in the urine. The kidneys of a myeloma patient may be damaged by. The urine volume and urinary and fractional sodium excretion were not significantly different from the right kidney.
Blood urea nitrogen BUN level is another indicator of kidney function. A creatinine and Blood Urea Nitrogen BUN blood test outside the normal range. High blood calcium levels that result from the breakdown of bones.
Normal creatinine clearance for healthy women is 88-128 mLmin. In the D2-untreated group the GFR and RBF of the left obstructed kidney were 76 and 72 that of the right non-obstructed kidney 099 006 vs. 130 008 P 005 and 425 033 vs.
Learn about each of these tests and how they are used to diagnose and monitor your disease and kidney function. There were significant improvements in all three measures of renal function. Glomerular filtration rate is the best overall indicator of kidney function.
However raised uric acid is a bad prognostic indicator for chronic renal disease. Urea is also a metabolic byproduct which can build up if kidney function is impaired. The most frequently determined clinical indices for estimating renal function depends upon concentration of urea in the serum.
GFR provides the best estimate of functioning renal tissue. What lab is the best indicator of renal function. Although many forms of kidney disease do not produce symptoms until late in the course of the disease there are six warning signs of kidney disease.
Urine tests can also detect whether the kidneys are leaking abnormal amounts of protein a sign of kidney damage. Protein intake and Liver Function the test is usually done in conjunction with Plasma Creatinine which is a more specific indicator of kidney function. Contraction of glomerular mesangial cells What is autoregulation.
In respect to this do kidney problems show up in blood tests. Loss of appetite Fatigue and weakness Changes in urinating Muscle twitches and cramps Persistent itching What causes Kidney Disease. GFR is a measure of kidney function and is performed through a blood test.
An elevated BUN by itself is suggestive but not diagnostic of kidney dysfunction because BUN can be affected by other factors. Normal 10 to 15 mgdL Creatinine clearance GFR Creatinine clearance It estimates the renal excretion or filtering capacity of the kidney. Creatinine is a waste product that comes from the normal wear and tear on muscles of the body.
Renal function test The following parameters are commonly included in assessing renal function the normal valuesreference range is mentioned Serum Urea 15-45 mgdl. Markers of kidney damage one or more GFR 60 mLmin173m2. Heres a quick guide to the tests used to measure kidney function.
Age 60 or older GFR declines normally with age. Estimated glomerular filtration rate eGFR. Glomerular Filtration Rate GFR Factors that affect the GFR Changes in renal blood flow afferent or efferent arteriolar diameter perfusion pressure.
Serum Creatinine and Blood Urea Nitrogen. Urine electrophoresis UPEP of a sample from a 24-hour urine collection. Your kidney numbers include 2 tests.
What is normal kidney function level. Urine albumin is the first test to be performed in diabetics to determine renal function. If symptoms do occur some common indicators include.
Perioperative assessment of renal function Urine flow rate specific gravity and osmolality are all poor indicators of renal dysfunction because they are influenced by nonrenal factors. Serum creatinine more reliable indicator of renal function than BUN because BUN can change with volume status. Which of the following are indicators of renal function.
Normal Male 97 to 137 ml minute Female 88 to 128 ml minute. Know your kidney numbers. Although novel biomarkers are in practical use serum creatinine the indicator of glomerular filtration rate is still the most frequently used biomarker of renal function despite its.
And 97 to 137 mLmin. BUN and creatinine are good screening tools but poor tools to predict renal dysfunction because they are late warning signs of declining renal function. In males normal levels may vary slightly between labs.
Intravenous hydration volume and renal function indicators serum creatinine sCr blood urea nitrogen BUN glutamate oxaloacetate transferase glutamate pyruvate transferase and uric acid levels. Testing in a Laboratory Initial diagnosis of acute or chronic illness is made using serum creatinine blood urea nitrogen BUN and estimated glomerular filtration rate EGFR. GFR provides the best estimate of functioning renal tissue.
The corrected GFR is approximately 8 lower in women than in men and declines with age at an annual rate of 1 mLmin173m 2 from the age of 40. The most statistically significant improvement and with the most complete data set occurred in serum creatinine this reduced by a mean SD of 47 149 μmolL P 00000054. CKD risk factors include but are not limited to the following.
Light chain monoclonal proteins. Either of the following must be present for 3 months. What is the best indicator of renal function.
Local mechanism that keeps GFR fairly constant. It is useful in differential diagnosis of acute renal failure and pre renal condition where blood urea nitrogencreatinine ratio is increased. Family history of kidney disease.
ACR Albumin to Creatinine Ratio and GFR glomerular filtration rate. Urine albumin Evaluation of the protein is a sensitive indicator of kidney function. This is the measure of kidney function.
Serum creatinine eGFR and urine ACR. 592 061 P 005 respectively. The normal corrected GFR is 80-120 mLmin173m 2 impaired renal function is 30-80 mLmin173m 2 and renal failure is less than 30 mLmin173m 2.
Damage to the glomerular membrane or loss of nephrons leads to a corresponding decrease in GFR. Renal impairment both in the form of acute and chronic renal failure could be severely harmful and even life-threatening for the patient in the absence of an early diagnosis 1For this reason physicians must obtain a thorough patient history and determine the presence of underlying disorders that may induce renal impairment whereas a complete physical examination. Serum creatinine and BUN are useful indicators of renal function.
Pathogenesis Diagnosis And Treatment Of Renal Dysfunction In Cirrhosis

Comparison Of Gates Gfr With Mdrd Gfr For Various Range Of Renal Function Download Table
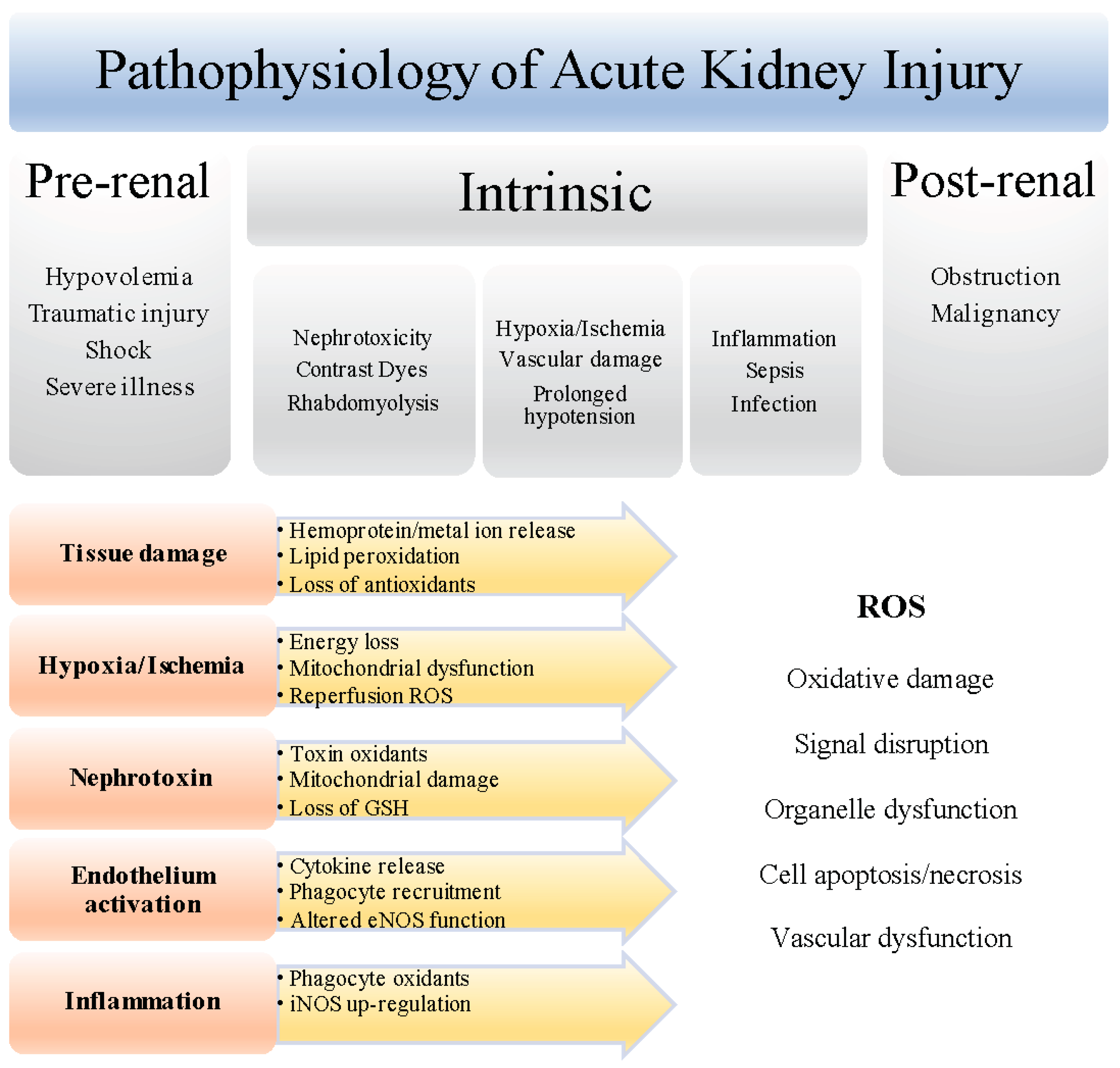
Nutrients Free Full Text Protective Role For Antioxidants In Acute Kidney Disease Html

Five Stages Of Chronic Kidney Disease Based On The Estimated Glomerular Download Scientific Diagram

Kidney Disease A Straightforward Diagnostic Approach Kidney Disease Nursing School Notes Renal Physiology

Pdf Definition And Classification Of Chronic Kidney Disease A Position Statement From Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes Kdigo
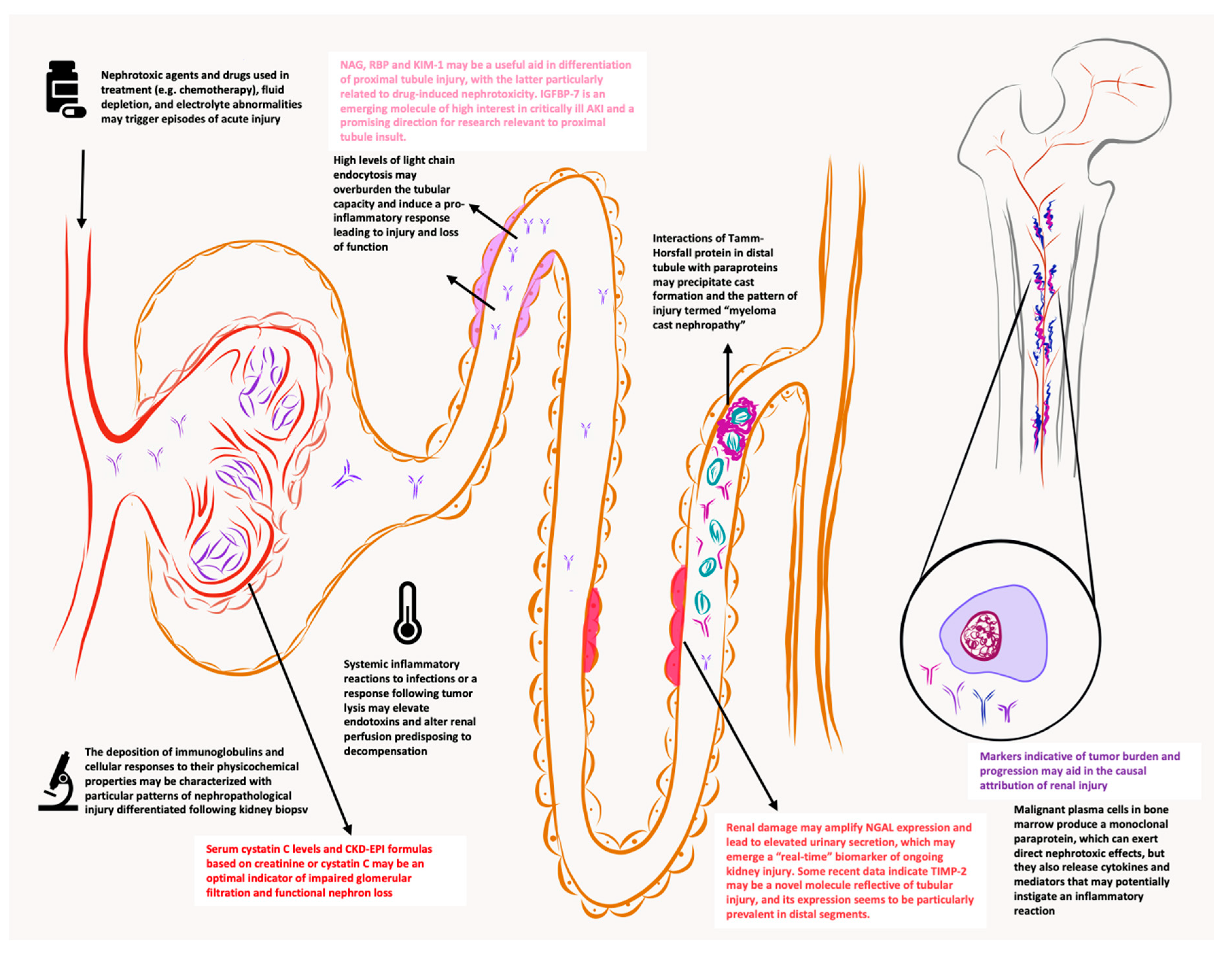
Jcm Free Full Text New Markers Of Renal Failure In Multiple Myeloma And Monoclonal Gammopathies Html
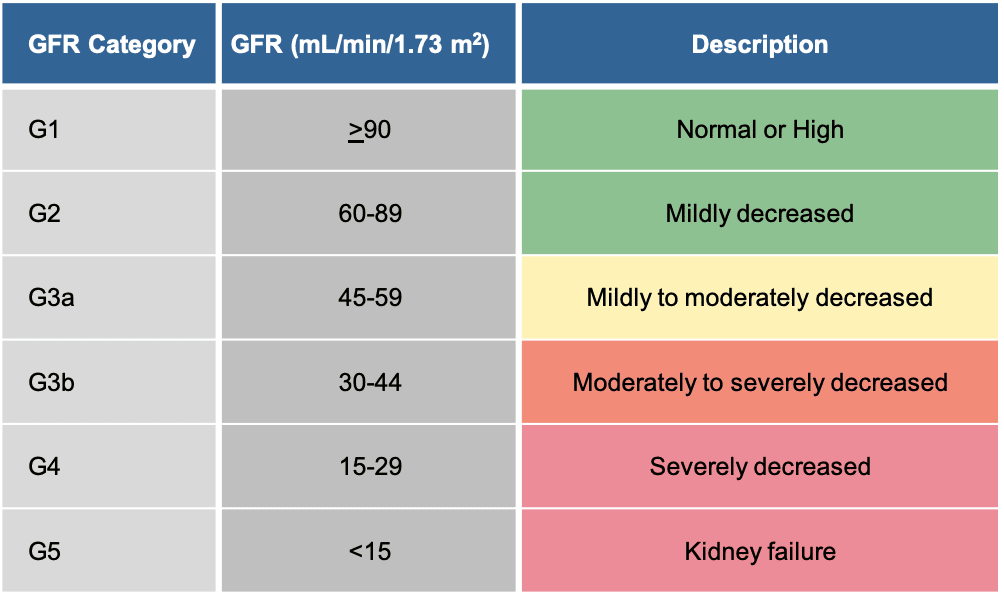
Core Concepts Treatment Of Hcv In Persons With Renal Impairment Treatment Of Key Populations And Unique Situations Hepatitis C Online

Liver Function Test Renal Function Test Download Table
Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care And Management Study Guide

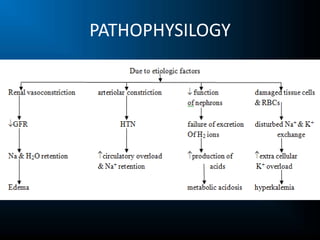
Aetiology Of Acute Renal Failure Download Scientific Diagram

Formulas To Calculate Glomerular Filtration Rate Gfr As A Measure Of Download Table

7 Signs That You Might Have Kidney Disease Kidney Disease Renal Disease Kidney Disease Stages
Pathogenesis Diagnosis And Treatment Of Renal Dysfunction In Cirrhosis



Comments
Post a Comment